LIVING THINGS
- The term living thing refers to things that are now or once were alive
- A living thing pertains to any organism or a life form that possesses or shows the characteristics of life or being alive
PLANTS
- Plants are living things.
- The grouping of plants together with common characteristics or features is called the classification of plants.
TYPES OF PLANTS
Identifying different types of plants
Pupil’s activity Page 1
To observe the different types of plants
Pupil’s activity Page 1
To identify different types of plants found in the locality
Pupil’s activity Page 2-3
Types of plants found in the locality
- Trees
- Are big plants
- They have single stem called trunk and many strong branches
- Examples of tress include mango, coconut and avocado trees
- Shrubs
- Are shorter than tress
- They have many thin and woody stems
- Examples of shrubs include hibiscus, rose and cotton plants
- Shrubs
- Are small plants with soft green stems
- Examples of herbs include mint and coriander
- Grass
- Is short and has narrow leaves
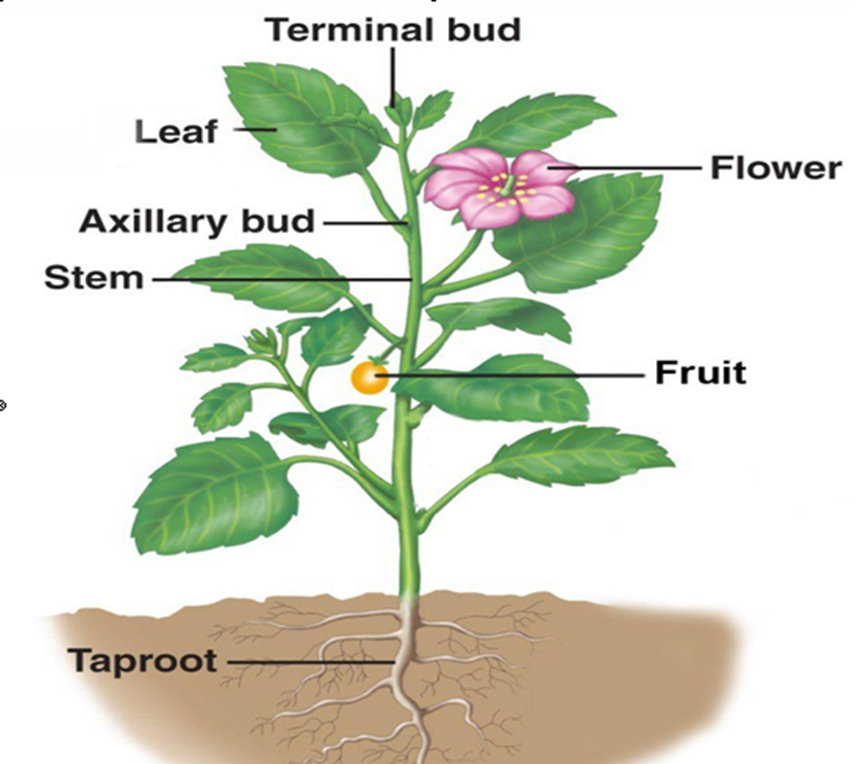
Parts of a Plant
Identifying different parts of a plant
To name different parts of a plant
Pupil’s activity Page 3
To identify different parts of plants growing in the environment
Pupil’s activity Page 3-4
To draw different parts of a plant
Pupil’s activity Page 5
- The external parts of a plant include
- Roots
- Stem
- Leaves
- Flowers
- Fruits 6.
Functions of different parts of a plant
To discuss the functions of different parts of a plant Pupil’s activity
Page 6
| Part of a plant | Function |
| Leaves | |
| Stem | |
| Fruits | |
| Seeds | |
| Flowers |
Functions of the roots
- Support/hold/anchor the plant firmly in the soil
The roots absorb water and mineral salts from soil through a process called absorption Plants need water and mineral salts for proper growth
- Absorption of water and mineral salts
The roots hold the plants firmly in the soil
This ensures that the plants are not carried away by water or wind
- Food storage
Some plants such as arrowroots, cassava and carrots store food in the roots
Functions of the stem Stem –
- Transports water and mineral salts from the roots to the leaves Carries food made by the leaves to the roots for storage
- Holds or supports the upper parts of the plant in good position
- Protects the plant
- Storage of water- some plants such as a cactus store water in the stem
- Some stems store food and water for the plant
N.B. Plants that store food in the stem are called stem tubers. Examples of plants that store food in the stem are: a) Cactus b) Sugar cane c) Irish potato
To investigate the absorption and transport of water and mineral salts in a plant
Pupil’s activity Page 7-8
Free Grade 6 Science And Technology Lesson Notes
Functions of the leaves
- Breathing – Exchange of gases through small tiny holes called stomata.
- Manufacture of food
Leaves make food for the plant using chlorophyll, sunlight, water and carbon (IV) oxide through a process called Photosynthesis – Process of making its own food Requirements of photosynthesis are:- Chlorophyll – green colouring matter Water Carbon dioxide Sunlight
- Storage of food – Edible vegetables such as kales, cabbages, spinach
- Removal of excess water through transpiration
Transpiration – Process in which plants lose excess water through small holes called stomata. Transpiration is high when it is hot, sunny, dry, windy. It is low when it’s cold, wet, calm and rainy.
Function of flowers
- Flowers are the reproductive organs of plants
- They develop into fruits
- It bears fruits which contains seeds that germinate into a new plant Seeds germinate into new young plants called seedlings
Function of fruits
- Storage of food
Some plants like avocados, mangos and orange store food in fruits
- Protecting seeds
In most plants, seeds are found inside fruits The fruits protect the seeds from drying
Functions of seeds
When seeds germinate, they grow into new plants
To investigate transpiration in plants
Pupil’s activity Page 9
Making mounts of plants
Pupils activities Page 10-11
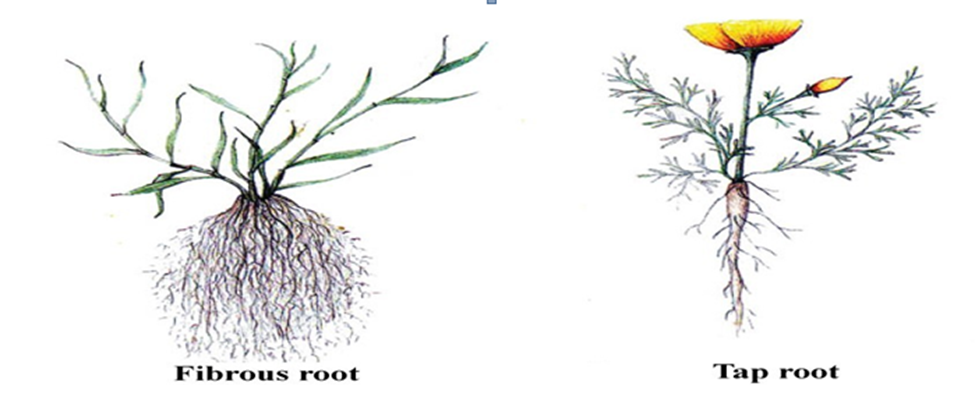
TYPES OF ROOTS
There are two main types of roots
- Tap root – extension of stem with side roots
- Fibrous roots-many similar roots
To observe taproots and fibrous roots
| Taproots | Fibrous roots |
| They consist of one main root that grows down into the soil They have lateral roots that arise from the main root | They do not have a main root All roots are similar and they arise from the same place |
| They grow deep into the soil | They are shallow |
| They grow vertically downwards into soil | They grow horizontally in all directions |
| Plants with tap roots include:- Legumes, Acacia, Fruit trees, | Plants with fiirous roots include:- Cereals, Oats, Grass, Sisal, Onions, Sugarcane, Coconuts |
Grouping plants based on the type of roots they have
Pupil’s activity Page 16
Other types of roots
Other types of roots include:
- Aerial roots – for breathing
- Prop roots – used in maize for support
