SCIENTIFIC INVESTIGATION IN BIOLOGY
Collection of Specimen
We have defined biology as the study of living things. For effective study, a biologist may have to collect some living things or some parts of living things for observation and analysis. The living things or parts of living things that are used for biological study are called specimens. Biological studies always take place in laboratories. A laboratory is a building or a room that is designed and equipped for scientific studies. Collections of living things especially animals may not be very easy. Some of the animals are not easy to catch while some are quite dangerous. Knowledge on proper specimen collection and handling of is very important. We will discuss some of the apparatus used in specimen collection.
1. Apparatus for Specimen Collection and Preservation
Apparatus/Material Use
Pooter/Aspirator Sucking small insects safely
Pitfall trap Trapping crawling insects or animals
Soapy water Used in traps for drowning insects
Forceps Picking small specimens without damage
Sweep net / Aerial net Catching flying insects
Light trap Attracting and trapping nocturnal insects
Tullgren funnel Extracting small animals from soil/litter
Envelopes Holding butterflies or moths
Labels & Permanent Ink Marking collected specimens
Hand lens Magnifying small features
Tracing paper Drawing and recording features
Gloves and Digger Safe and effective soil specimen collection
Apparatus/Material Use
Knife or Secateurs Cutting plant parts
Collecting bags Transporting specimens
- Sweep net
This is used for catching flying insects.
- Fish net
This is used for trapping small fish and other small water
- Pooter
This is used for sucking small animals from rock surfaces or barks of trees.
Bait trap
This is used for attracting and trapping small animals including rats.

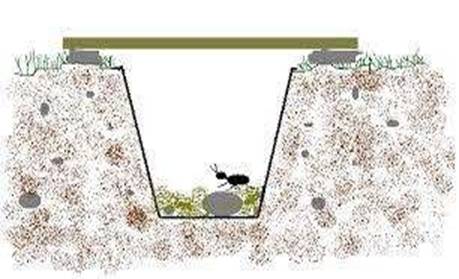
- Pit fall trap
This is used for catching crawling animals.
- Pair of forceps
This is an apparatus used for picking up small crawling animals e.g. stinging insects.

- Specimen bottles
These are bottles used for keeping collected specimen. They are of different sizes depending on the size of the specimen being studied.

- Magnifying lens
This is used to enlarge small objects. A hand lens is a common magnifying lens used in the laboratory. The magnifying power of the hand lenses is always indicated on the lens e.g. X10, X5, X8. The magnifying power of a lens shows how many times the image will be enlarged compared to the object.

How to use a magnifying lens
-To use a magnifying lens, place the object to be enlarged on the bench. Hold the magnifying lens on one
hand and while closing one eye, move the lens towards the object until the image comes into clear focus.
-If a magnifying lens is used to make a drawing of a specimen, the magnification of the drawing will have no
relation with the size of the drawing.
The magnification of the drawing can be calculated using the formula shown below.
Drawing magnification= length of drawing/length of actual object
The multiplication sign must come before the magnification value e.g. X10, X5, X15 etc.
Precautions During Collection and Observation of Specimen
While collecting specimen for observation, a biologist should play close attention to the following:
Collect only the number of specimen you need; do not collect more than you need.
Do not harm the specimen during the capture/collection exercise.
Do not destroy the natural habitat of the specimens.
Handle dangerous/injurious specimens with care. Such injurious specimens can be stinging plants or insects.
Forceps and hand gloves should be used in such cases.
Techniques in Collection, Processing, and Preservation
- Plant Specimens
- Collection: Use secateurs/knife to cut leaves, flowers, or small branches.
- Processing: Press using blotting paper and weight.
- Preservation: Dry, mount on paper, and label (common name, scientific name, locality).
- Storage: Keep in dry, insect-free environments.
- Animal Specimens
- Collection: Use pooters, nets, pitfall traps depending on size/type.
- Processing:
- Sort by type.
- Mount on soft boards (for insects).
- Preservation:
o Use ethanol or formalin (wet preservation). o Label properly (name, date, locality).
Project-Based Learning (PBL) – Specimen Collection Project Requirements:
- Plan the project (set objectives, timeline, and resources).
- Budget (include transport, containers, materials).
- Collect both plant and animal specimens.
- Record and document each step (photos, labels, notes). Reflect and present to class or school science fair.

