What is a Portfolio?
A portfolio is a systematic, integrated and meaningful collection of a learner’s day-to-day classroom work or artifacts that provide a visual of their own learning, progress, and achievement.
It provides evidence of achievement or mastery over a period of time
Importance of a Learner’s Portfolio
It enables learners to show quality of work in collaboration with others;
Instructional goals are set at the beginning and shared with the learner;
Provides a clear profile of learners in terms of abilities and interests;
It allows demonstration of a wide range of competencies;
It demonstrates leaner’s progress over time;
It gives learners an opportunity to reflect on their work, and;
It enables learners to demonstrate their creativity.
Component of a Good Portfolio
A cover page;
Table of content
Entries in form of drafts or completed work, dates and;
Reflections on the items presented.
Note: A portfolio can be physical (manual) or electronic (e-portfolio
Stages of Developing a Portfolio
Planning
Type
Audience
Storage
Communication
Collection of work samples
Selection of work samples
Reflection
Feedback
Effective Management of a Portfolio
Review entries in the portfolio with learners regularly;
Focus more on quality than quantity;
Involve the learners in organizing the portfolio, and;
Organize for the storage of the learners’ portfolios.
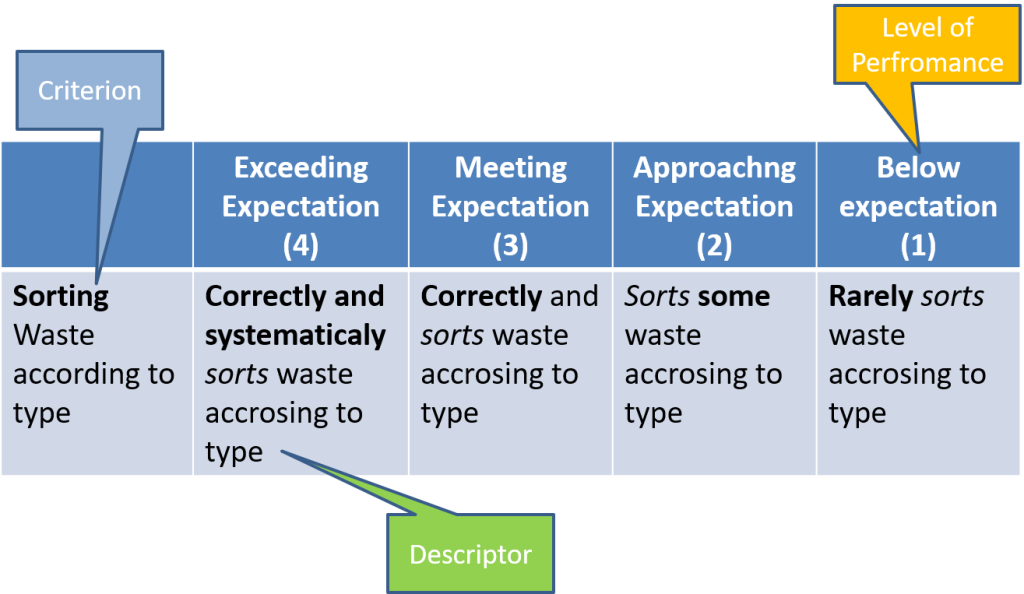
What isAssessment Rubrics
- Rubric consist of a set of score points and related descriptors that articulate the criteria and performance levels in a learning arranged in a measure of quality.
- The criterion describes what a completed piece of work looks like.
- Grading should be solely based on learners’ achievement in meeting the learning outcomes of the subject areas.
Components of a Rubric
Types of Rubrics
- Analytic Rubric
Breaks down content or tasks being assessed into parts.
Assesses each part separately - Holistic Rubric
Assesses overall performance on a task as a single entity.
Scores the overall competencies of the learner

