NATURAL AND BUILT ENVIRONMENTS
Position and Size of Countries in Eastern Africa
Countries in Eastern Africa
- Eastern Africa is the region located in the eastern region of Africa.
- It is made up of eleven independent countries namely:
- Sudan
- Ethiopia
- Tanzania
- Somalia
- South Sudan
- Kenya
- Uganda
- Eritrea
- Burundi
- Rwanda
- Djibouti
NB
- Sudan is the largest country in eastern Africa
- South Sudan became independent in JULY 2011 Ø Djibouti is the smallest country in eastern Africa
- Countries without a coastline are called landlocked e.g. Burundi, Uganda, Rwanda, Ethiopia and South Sudan.
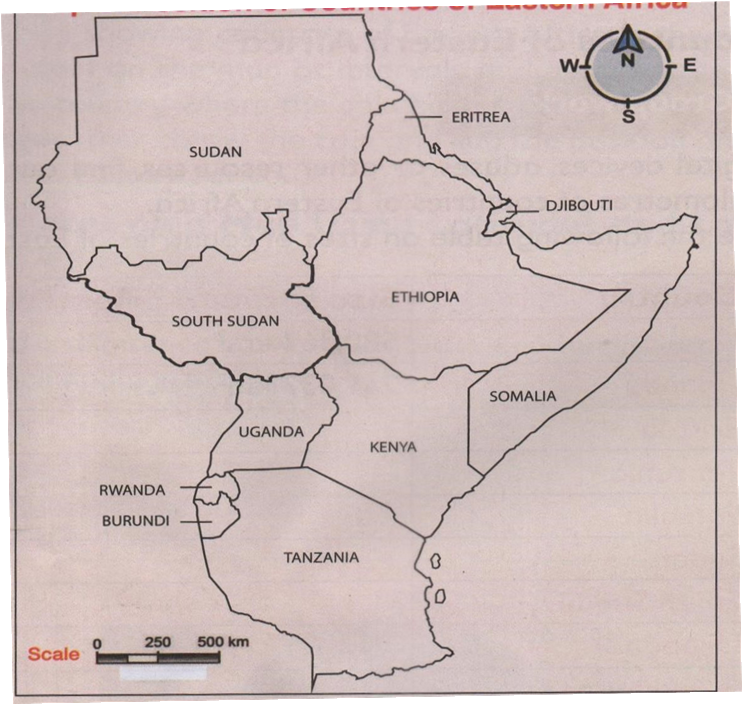
POSITION OF COUNTRIES OF EASTERN AFRICAN
- Using a compass you can locate position of a country in relation to her neighbours.
- Kenya lies to the -:
- North east of Tanzania
- South of Ethiopia
- South east of South Sudan,
- East of Uganda
- West of Somalia
- Immediate neighbours of Kenya are Tanzania, Uganda, South Sudan, Ethiopia, and Somalia.
SIZE OF THE COUNTRIES OF EASTERN AFRICA
| COUNTRY | SIZE in square kilometres (km2) |
| Sudan | 1.886 million km2 |
| Tanzania | 945,087 km2 |
| Somalia | 637,655 km2 |
| South Sudan | 644,329 km2 |
| Kenya | 580,367 km2 |
| Uganda | 241,037km2 |
| Eritrea | 117, 598 km2 |
| Burundi | 27,834 km2 |
| Rwanda | 26, 338 km2 |
| Djibouti | 23,200 km2 |
| Ethiopia | 1.104 million km2 |
LOCATING PLACES ON A MAP USING LATITUDES AND LONGITUDES
- Eastern Africa lies within latitudes 22 ̊N AND 12 ̊S and between longitudes 22 ̊E and 51 ̊E/52 ̊E.
Latitudes
- These are imaginary lines that runs from west to east
- They are also called parallels
- The main line of latitude is equator at 0 ̊
- Equator divides the earth into two equal halves called hemisphere.
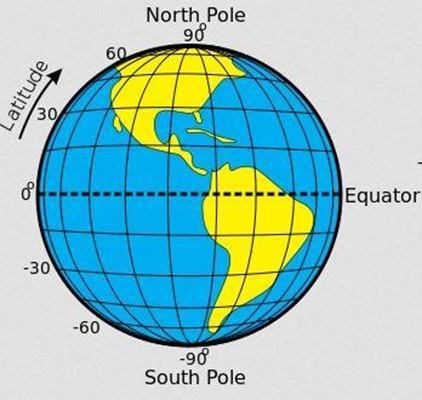
Characteristics of latitudes
- They are parallel
- They are of different lengths
- They affect climate
- They are measured in degrees from the equator
- They are 180 lines of latitudes in total
Latitudes lines are; Equator at 00
- The tropic of cancer 23 ½º N
- The arctic circle 66 ½ ̊ N
- The tropic of Capricorn 23 ½º S
- The Antarctic circle 66 ½º S
LONGITUDES
- These are imaginary lines that run from North Pole to south pole of the earth
- They are also called meridians or horizontals
- Main line of longitude is Greenwich meridian at 0 ̊
- Greenwich meridian is also called prime meridian
- Prime meridian passes through the Greenwich town in London and Accra in Ghana
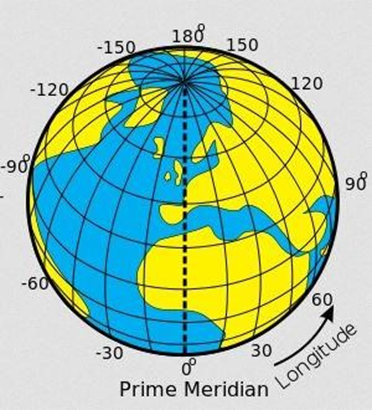
Characteristics of longitudes
- They run from north to south
- They are not parallel
- They meet at the poles they affect time
- They are of the same length
- They are measured in degrees east por west of prime meridian
- They are 360 ̊ lines of longitudes in total.
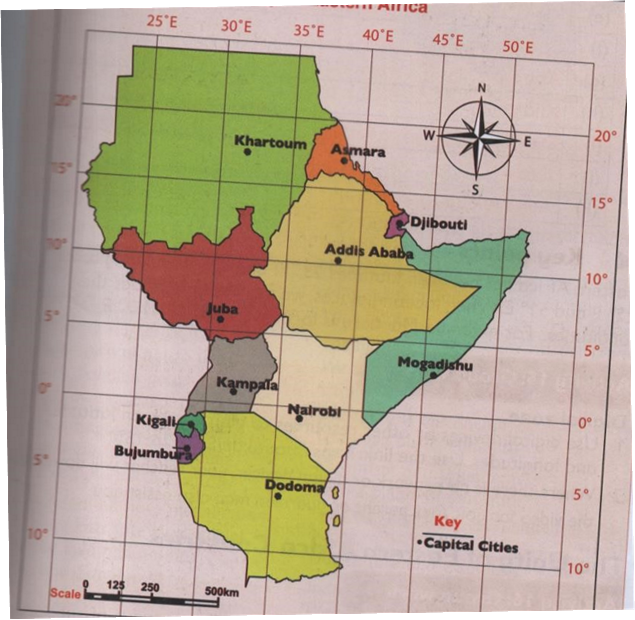
| TOWN | LOCATION | |
| 1 | Nairobi | 1.3º S, 36.8ºE |
| 2 | Dodoma | 6.5738 S, 6.2631º E |
| 3 | Kampala | 0.3634º N, 32.6051º E |
| 4 | Mogadishu | 2.0º N, 45.3º E |
| 5 | Kigali | 1.9441º S, 30.06º E |
| 6 | Bujumbura | 3.36º S , 29.3599º E |
| 7 | Asmara | 15.3381º N, 39.9318º S |
| 8 | Khartoum | 15.30º N, 32.31º E |
| 9 | Djibouti | 11.8251º N, 42.5903º E |
| 10 | Juba | 0.2240º N, 41.6012º E |
| 11 | Addis ababa | 8.9806º N, 7578º E |
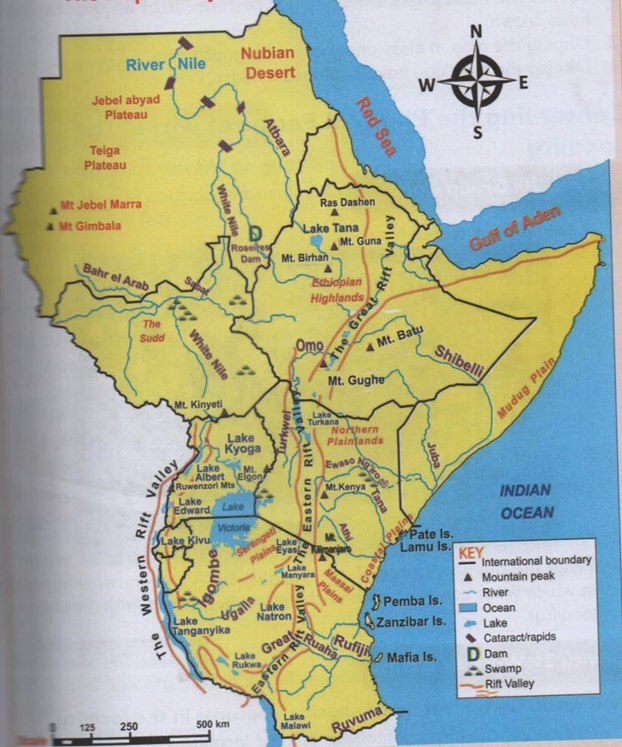
MAIN PHYSICAL FEATURES IN EASTERN AFRICA
Physical features are naturally things found on the surface of the earth They include:
- Mountains
- Valleys
- Plateaus
- Ocean
- Seas
- Gorges
- Plains
- Lakes
- Rivers
- Swamps
- Hills, rangers
THE MAIN PHYSICAL FEATURES IN KENYA
1. Mountains
- Are masses of very high land.
- They are the highest physical features on the earth.
Major mountains in eastern Africa
| KENYA | TANZANIA | UGANDA | SUDAN | ETHIOPIA |
| Mt.kenya | Mt.kilimanjaro | Ruwenzori | Jabel-marra | Ras dashan |
| Mt.longonot | Mt.meru | Nubadarfur | Guna | |
| Mt.marsabit | Pare mts | Kissu | Danakil alps | |
| Mt .kulal | Ngorongoro crater | |||
| Menengai crater | Lool molasin |
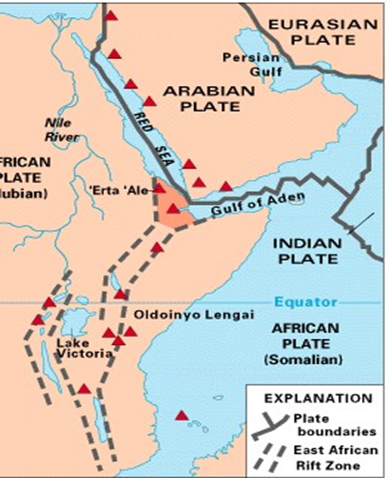
2. Rift valley
- A valley is a low lying are with steep slopes.
- In eastern African the rift valley has 2 branches that stretch across several countries
The two branches are the eastern rift valley and the western rift valley
3. LAKES
- A lake is a water body that is surrounded by land
- A hollow/depression filled with water
- We have 1) Fresh water lakes 2) sailty water lakes
- Main lakes in eastern Africa are
| KENYA | UGANDA | TANZANIA | ETHIOPIA | RWANDA |
| Turkana | Albert | Natron | Chamo | ruhondo |
| Baringo | Edward | Manyara | Abaya | kivu |
| Bogoria | Bunyonyi | eyasi | Steffanie | |
| Nakuru | Bisini | Rukwa | Shala | |
| Elementaita | George | Malawi | tana | |
| Naivasha | Kyoga | tanganyika | ||
| Magadi | Kivu | |||
| Jipe | mutanda | |||
| Chala |
4. Plains
- Are low lying areas of almost flat land.
- Examples
| KENYA | UGANDA | TANZANIA | SOMALIA |
| Lotikipi, awara, kano, | Luwero | Serengeti | Bilesha |
| Kaputei, loita, | Nakasongola | maasai | Sarar |
| Budalangi,kapiti | Haded | ||
| bilesha |
FORMATION OF MAIN PHYSICAL FEATURES OF EASTERN AFRICA
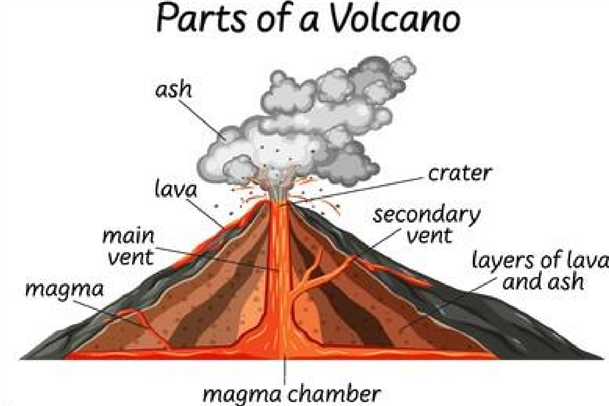
Formation of volcanic mountains
- They are also called volcanoes
- They are formed through the process of volcanicity/eruption.
- Eruption is when the hot molten material underground is forced out by great pressure
- The hot molten material is called magma
- When magma gets to the surface is called lava
- The magma gets out through a main pipe called vent
- The opening at the top of a volcanic mountain is called a crater Most mountains in eastern africa are volcaning mountains
| KENYA | UGANDA | TANZANIA | RWANDA |
| Kenya | Mt meru | Mt karisimbi | |
| Elgon | Mt Kilimanjaro | Nyiragongo | |
| Longonot | Ngorongoro | ||
| Menengai crater | Lool malsin | ||
| Marsabit | |||
| Suswa | |||
| Kulal |
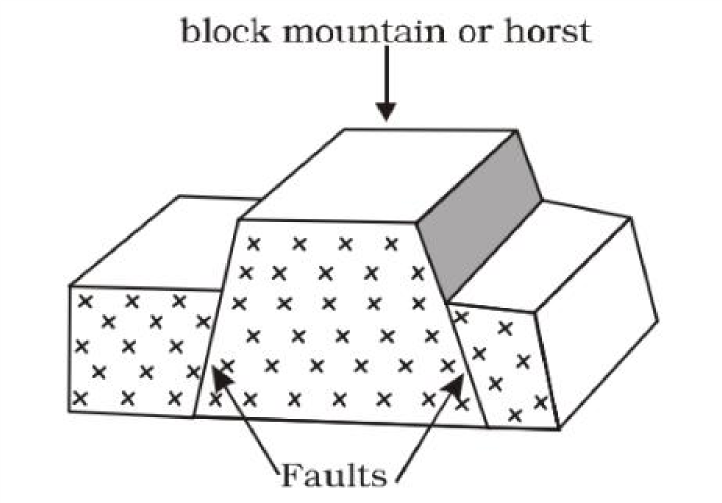
Formation of Block Mountains
- They are also called horst mountains
- They were formed through faulting and uplifting process
- Faults are lines of weakness
- Faults were developed as a result of forces acting on the layers of the earth
- The forces involved are tensional and compressional forces
- The middle block was pushed upward by underground forces
- The underground forces called up thrust force Examples
| ETHIOPIA | UGANDA | TANZANIA |
| Danakali alps | ruwenzori | Pare |
| usambara |
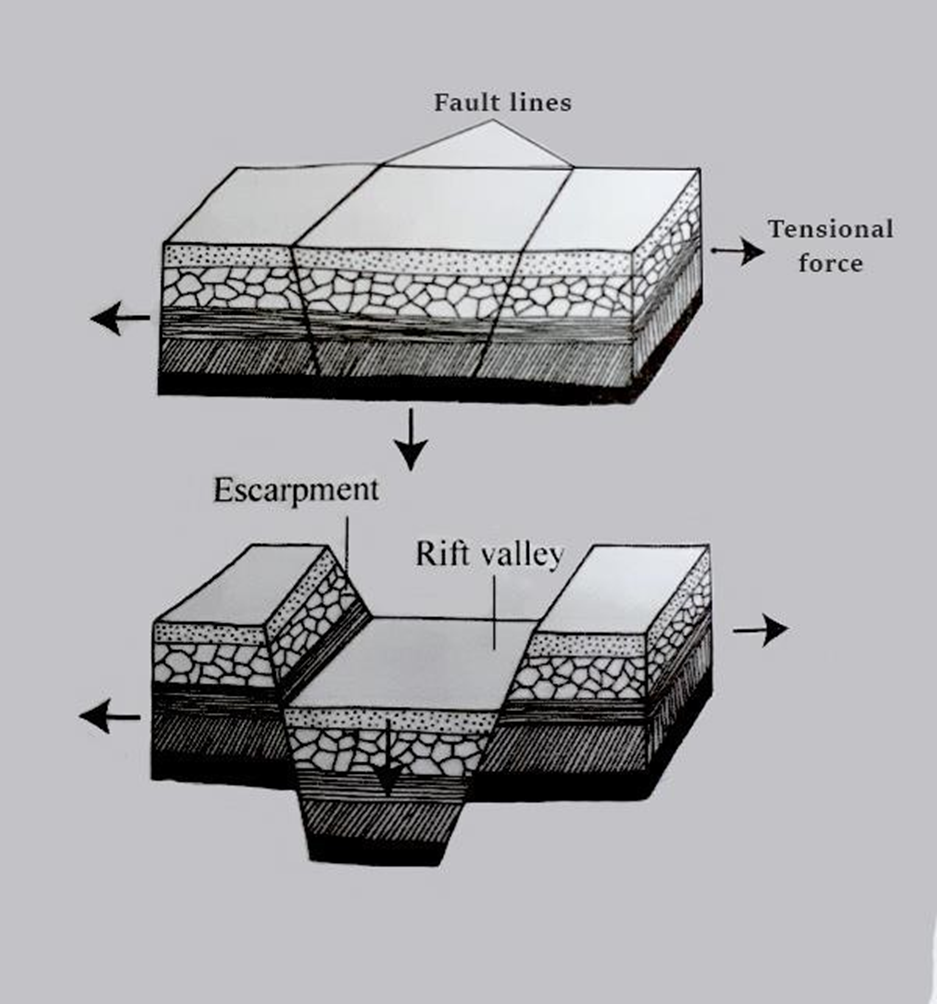
Formation of the rift valley
- The rift valley was formed when two cracks or fault line formed within the crustal rocks
- The land between the two faults sunk forming a valley
- Was formed through the faulting process
- Formed by either tensional or compressional forces
- When two parallel faults developed the tensional forces pulls the rocks apart
- The middle block between the faults sink
- The steep sides of a rift valley are called escarpments
Formation of lakes
The major lakes in eastern African were formed as a result of
- Faulting
- River deposition
- Down warping
- Volcanicity
1. Rift valley lakes
- During the formation of the rift valley, some parts of the land sunk deeper than others forming depressions.
- The depressions were filled with water to form lakes
- Example – lake Tanganyika in TZ
2. Lakes formed as a result of down warping
- Down warping is a process by which the earth sinks inwards due to pressure forming a big basin.
- Water fills this basin to form a lake.
Example: lake Victoria in Kenya
3. Lakes formed as a result of volcanicity a. Lava dammed
- Lava dammed lakes are formed when lava flow on the surface of the earth and comes int contact with a river, blocking it
- This leads to the formation of a lake
Example: lake kivu in Rwanda
b. Crater lakes
- When volcanic eruption occurs, the top of the mountain may be blown of forming a hallow depression called crater.
- Water fills the hallow depression forming a crater lake.
Example; Lake paradaise in Kenya, Ngozi in Tanzania and Shalla in Ethiopia.
Formation of plains
- Plains are wide low lying areas of flat land.
- Plains are formed as a result of erosion and deposition of the eroded materials.
MAP OF EASTERN AFRICAN SHOWING MAIN PHYSICAL FEATURES
CONSERVING THE PHYSICAL FEATURES WITHIN THE LOCALITY
We should protect and conserve physical features found in our locality
- Prevent overuse and deforestation of forest.
- Avoid pollution of water bodies.
- Educate people on importance of physical features.
