COMPUTER SCIENCE LESSON NOTES
FOUNDATION OF COMPUTER SCIENCE
Computer concepts
Definition
- Computer
An electronic device that accepts data from a user, Processes the data using given instructions, stores it and presents it in a desired format
- Data
Raw facts which include numbers, texts, images, audios or videos that input into a computer
- Information
Data that has been processed and made meaningful to the user
Examples of computers
- Notebooks
- Smartphones
- Macbook
- PDA
- Desktop computer
- Laptop
- Ipad
- Tablet
- Smartwatch
- Server
- Each examples of computers have different features that enable them to serve different
Characteristics of a computer
- Speed
A computer works at a higher speed than human beings
- Storage
Computers have storage space that can hold large amounts of data and information
- Multitasking
Computers can perform more than one tasks at the same time
- Accuracy
Computers give information without errors if given the correct data and instructions
- User dependant
Computer cannot work without instructions from the user
- Versatility
Computers have ability to perform a variety of task(complex and simple)
- Reliability
The electronic components in modern computer have very low failure rate. The modern computer can perform very complicated calculations without creating any problem and produces consistent (reliable) results.
- Diligence
Computers, unlike frail human beings, do not become bored or tired or lose concentration when performing highly repetitive work. If a computer has to perform a certain calculation on a million numbers, it will calculate the first and the last with equal diligence. This enables trust to be placed in the results generated by computers, and confidence to be replaced in their ability – neither of which can always be replaced in humans!
Function of a computer
- Stores data and information
- Process data into information using given instructions
- Accepts data from the user
- A computer gives out information to the user
Uses of computers to perform daily activities
- Accessing internet
- Paying online bills
- Home/school tutoring
- Stock taking
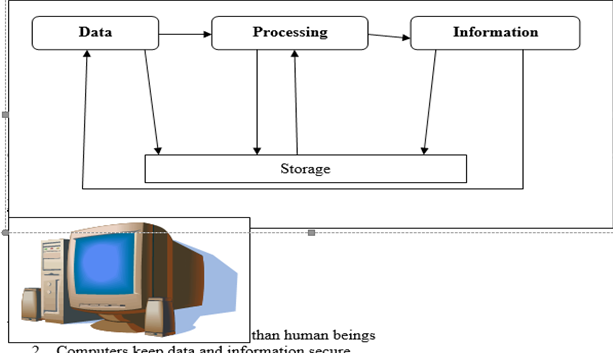
Stages of computer processing cycle
- Computers keep data and information secure
- Computers can store a lot of data in a small physical space
- Computer can do the same repeatedly without getting tires or bored
- Computer are able to perform different types of jobs at the same time
- A computer is reliable because it consistently does what it is supposed to do.
- Computers have a very big storage capacity and can store data and information for a very long time
- Information given by computers after processing has no error because they work under instructions and are always accurate
Computer processing cycle is the stage or events that takes place from the time data is entered into the computer to the time is given to the user.
Advantages of using a computer
- Computer process data faster than human beings
- Computers keep data and information secure
- Computers can store a lot of data in a small physical space
- Computer can do the same repeatedly without getting tires or bored
- Computer are able to perform different types of jobs at the same time
- A computer is reliable because it consistently does what it is supposed to do.
- Computers have a very big storage capacity and can store data and information for a very long time
- Information given by computers after processing has no error because they work under instructions and are always accurate
Disadvantages of using a computer
- Use of computer has caused people to lose jobs because computers process data within a shorter time
- Use of computers for long hours leads to health problem like headaches, eye strains
- Computer lack intelligence. They cannot determine what is wrong or right. If given wrong data, they give out wrong information
- People sometimes become too dependent on computers. This affects their creativity and ability to do simple tasks
- Information and data stored in computers is at risk of theft and misuse
- People use the internet to perform online crimes and fraud
- Online threats such as cyber bulling are on the increase with the increased use of computers and the internet
- Electronic waste from computers contains chemicals that destroy the environment
Application areas of computers
- Education
- For online reading
- To maintain class notes and registers
- For research and to do assignments
- Business
- To make payments
- To keep records
- To order for goods
- To sell goods and services online
- Banking
- To facilitate online and internet banking
- To operate ATM machines
- For money transfer from one bank to another
- To keep account and customer information
- Health care
- To conduct research
- To store patient data
- Manufacturing
- To model and design products for example airplane
- To test functionality of machines they are manufactured
- To automatic process in manufacturing companies
- Government
- To offer government services online through platforms such as Nemis and ecitizen
- To store data and information
- Communication
- To send and receive messages
- For making video and voice calls
- Engineering design
- To design houses, roads and buildings.
Engineers and designers use programmes like computer aided design for designing
- Marketing
- Marketing of goods and services
- To design and create marketing content
- Insurance
- Computers are used to keep records about customers
- Computers are used to manage money transactions
- Home
- For entertainment like watching movies
- For security purpose like storing and displaying data from CCTV cameras
Evolution of computers
Evolution stages of computers
Computers have evolved from the abacus to digital devices
- The Abacus
It is believed to have been invented 4000years ago
It was made of a wooden frame with rods fitted across, with round beeads that slide along the rod
- Mechanical devices
Napier’s bones – 1617
Pascaline or pascal’s calculator – 1642
Stepped reckoer 1671-1674
Jacquard loom 1801-1804
Difference engine 1820-1822
Analytical engine 1834-1838
- Electromechanical devices
Tabulating machine 1880-1888
Atanasoff – berry computer ABC 1937-1942
Mark 1 – 1937 1944
- Electronic digital computers
Digital computers are now classified into five generations with each having improved from the previous one
Tasks performed by computers at different evolution stages
| Type | Computer | Task performed |
| Abacus | Abacus | It performed calculations like addition and subtraction |
| Mechanical devices | Napier’s bones – Pascaline or pascal’s calculator – Stepped reckoer Jacquard loom Difference engine Analytical engine | They performed arithmetic calculations like addition, subtraction, division and multiplication. They automated tasks The analytical engine had a store processor (mill) and printing components |
| Electromechanical devices | Tabulating machine Atanasoff – berry computer ABC Mark 1 | They solved fairly complex calculations They complied and analysed statistical information They solved calculations based on instructions given |
| Electronic digital devices | Personal computer Desktop computer Laptops Smartphones | They performed complex tasks such as mathematical calculations, word processing, data storage and analysis and communications |
Difference engine and analytical engine
- The difference engine and the analytical engine were designed by Charles Babbage.
- The difference engine was a simple calculator
- When he was unable to complete the difference engine, he started on the analytical engine which was advancement of the difference engine
Difference between the difference engine and the analytical engine
| Difference engine | Analytical engine |
| Could perform only one mathematical operations | Could perform four mathematical operations |
| It had no input component | It used punch cards as input component |
| It had no storage component | Had a storage component |
| It had no processing component | Had an arithmetic unit called mill |
| It was a simple mechanical calculator | It was a general purpose computer system that could be fed with instructions to carry out operations automatically |
| It was faster than the analytical engine | It was slower than the difference engine |
Using computer that existed at different evolution stages
Pupil’s activity
Page 17
Contemporary technology and sustained development of computers
| Device | Technology used |
| Abacus | Decimal number system where each rod represents a column and each column represents a place value Binary digit system used in computers today where a value is either 0 or 1 |
| Napier’s bones | Used rods made of ivory, wood, metal or bones to work out multiplication problems using position of a number on a rod |
| Pascaline or pascal’s calculator | Used gears technology to feed data into the computer Had a display bar where the user could see the number entered and the answer It had no storage |
| Jacquard loom | Used punched cards technology to feed data into the computer Had no storage |
| Stepped reckoer | used stepped drum gear which mechanised addition, subtraction, division and multiplication employed the decimal number system |
| Difference engine | Used steam power Used a set of cogs levers and punched cards Had a storage for data Was designed to stamp its answer on set metal Used decimal number system where each number from 0-9 was represented by position on toothed wheels |
| Analytical engine | It had a processor called the mill and a store It could be given instructions to make the work automatic using punched cards |
| Tabulating machine | Used punched card technology Used electric current to count data on punched cards |
| ABC | Used binary digits to represent data Performed calculations using electric current Had storage for data Had processor |
| Mark 1 | Used electric circuits Data was fed in using punched sheets or rolls |
| Digital devices | Use the binary number system Have larger processors Have large storage Use electrical components |
Generation of computers
Computer technology has been advancing in many ways since the invention of the first electronic digital computer
Identifying generations of computers
- 1ST generation 1940-1956
- 2nd generation 1956-1963
- 3rd generation 1964-1971
- 4th generation 1971-1980
- 5th generation 1980 – present and beyond
Characteristics of different computer generations
- Characteristics of 1ST generation computers 1940-1956
- Entered data using punched cards, paper tape and magnetic tape
- Produced information in form of print outs
- Were very expensive
- Were very large in size
- Used alot of power
- Produced a lot of heat
- Were very slow
Examples
ENIA
EDVAC
UNIVAC
IBM 701
1BM 750
- Characteristics of 2ND generation computers
- Increased data processing speed
- Were very expensive to buy
- Were more reliable as compared to the first generation
- Consumed less power
- Were smaller in size compared to the first generation
- Used punched cards to enter data
Examples
IBM 1620
IBM 7094
CDC 1604
CDC 3600
UNIVAC 1108
- Characteristics of 3RD generation computers
- Had faster processing speed than the previous generation
- Consumed less power and emitted less heat as compared to the other generation
- Became relatively cheaper and therefore available for commercial use
- Were smaller in size than the second generation
- Had larger storage for data
- Used a mouse and keyboard to enter data
- Were more accurate
Example
IB 360 SERIES
PDP
IBM 370 SERIES
- Characteristics of 4TH generation computers
- Were vry fast and more reliable
- Were cheap and more easily available
- Were much smaller in size and therefore portable
- Introduced the use of personal computers
- Were able to connect to the internet
- Had very to large storage up to several hundred megabytes
- Used a keyboard and a mouse to enter data
- Used screens and printers to five information
- Produced less heat and could be cooled using a fan
Examples
IBM 308 AND 4300 SERIES, STAR 1000, APPLE II CRAY
- Characteristics of 5TH generation computers
- Have very large storage capacity
- Can use more than one processor at the same time
- Can perform more than one task at the same time
- Are cheaper and readily available even for personal use
- Are much faster than other generation computers
- Led to development of AI artificial intelligence
- Are easier to use
Examples
Desktop
Laptop
Tablets
Applying technologies of different computer generations in daily life
| Computer generation | Computer Technology used | |
| First generation | Vacuum tubes | These computers used thousands of electronic gadgets called vacuum tubes They were used for storage, calculations and control |
| Second generation | Transistors | 2nd generation computers used smaller components called transistors They allowed the use of words in specifying instructions |
| Third generation | Integrated circuits | The 3rd generation used IC technology which is a single device containing many transistors |
| Four generation | Very large scale integration | During the 4th generation LSI and VLSI technology was used to pack thousands or millions of transistors on a single device |
| Fifth generation | Ultra large scale integration | The 5th generation of computers is based on ULSI. Millions of transistors are packed into one small device This has enabled the rise in the use of AI |
Classification of computers
Types of computers
There are different types of computers used different purpose
- Mini computers
- Mainframe computers
- Analogue computers
- Hybrid computers
- Special purpose computers
- Micro computers
- Super computers
- Digital computers
- General purpose computers
Analogue Computers:
The word “Analogue” means continuously varying in quantity. The analogue computers accept input data in continuous form and output is obtained in the form of graphs. It means that these computers accept input and give output in the form of analogue signals. The output is measured on a scale. The voltage, current, sound, speed, temperature, pressure etc. values are examples of analogue data. These values continuously increase and decrease. The analogue computers are used to measure the continuous values. The thermometer is an example of analogue device because it measures continuously the length of a mercury column.
Computer Science Grade 5 Notes
Digital Computers:
The word “Digital” means discrete. It refers to binary system, which consists of only two digits, i.e. 0 and 1. Digital data consists of binary data represented by OFF (low) and ON (high) electrical pulses. These pulses are increased and decreased in discontinuous form rather than in continuous form.
Hybrid Computers:
The hybrid computers have best features of both analogue and digital computers. These computers contain both the digital and analogue components. In hybrid computers, the users can process both the continuous (analogue) and discrete (digital) data. These are special purpose computers. These are very fast and accurate. These are used in scientific fields. In
hospitals, these are used to watch patient’s health condition in ICU (Intensive Care Unit). These are also used in telemetry, spaceships, missiles etc.
Supercomputer
Is the most powerful and fastest, and also very expensive
Mainframe computer
Are large-scale computers but supercomputers are larger than mainframe.
Mini computer
Are smaller in size, have lower processing speed and also have lower cost than mainframe
Microcomputers
Are known as personal computers or simply PCs
Are meant for personal use by single users eg laptop, PDA
Special purpose computer
Computers designed to carry out specific tasks eg ATM
General purpose computer
Computers that can perform most common tasks eg word processing
Criteria used to classify computers
| Classification of computers | ||
| By functionality | By size | By purpose |
| Analogue | Microcomputer | General purpose |
| Digital | Minicomputer | Special purpose |
| Hybrid | Mainframe | |
| supercomputer |
Appropriate computers to use in different situations
Pupil’s activity
Page 33
Use of embedded computers in daily life
An embedded computer is a computer designed to perform a specific function
Embedded computers are used in different devices for example
- ATM machines have a computer that facilitates withdrawal of money, cash deposit and checking bank balance
- Cars have computer system to control the realises of airbags when a sensor detects an accident
Embedded computers also sense when one applies emergency brakes and prevent the wheels of the vehicle from locking and skidding through antilock braking system
- Microwaves have a computer that commands the heating element to turn on and off.
It calculates time, display time and rotates the plate
- Mp3 and DVD players are able to store, read data and play music and videos
- Drones have computers that enable user to control them.
The computers in drones enable them to capture images and videos and transmit them to the users
- Digital watches have computers to display time in numbers and set an alarm clock
Using different types of computers in performing tasks
Pupil’s activity
Page 35-6
Computer user environment
Computer user environment is an area equipped with devices, facilities and other components that provide suitable conditions for the use of computers
Examples are cyber cafe and computer laboratories
Factors to consider when setting up a computer user environment
- Accessibility
Computer user environment should be set up in a place where the intended user can easily reach
- Good lighting
The room should be well it
- Ventilation
The environment should be well ventilated, have free circulation of air and be free from heat, dust and moisture which can damage a computer system
- Power source
A computer user environment should have a reliable source of power to prevent loss of data and damage of computers
- Space
The floor space should allow free movement of people using the computer user environment
- Security
A computer user environment should be secure with strong doors and windows.
It should also have system in place to prevent unauthorised access
- Fire fighting equipment
Should be available at all times in case of a fire
- User friendly
The computer user environment should be made user friendly by ensuring there is comfortable furniture
- Proper cabling
Should be done from the power sources to the devices
The cable must be insulated and laid away from busy areas of the room to prevent people from getting electrocuted or tripping
Resources for setting up a computer user environment
When setting up a computer user environment, you need
- Desks and chairs
- Computer system
- Extension cards and electrical cables
- Good lighting
- Printers
- Scanner
- Projector
- UPS
Safety precautions and practise in the computer user environment
- Do not eat or drink in a computer user environment
- Do not touch naked wires
- Only allow authorised people. Avoid welcoming strangers
- Organise your desks before leaving
- Enter and exit quietly from the computer user environment
- Do not rush or push each other
- Avoid carrying pointed objects near computers
- Remove shoes entry to minimise dust
- Always follow the proper procedure for starring and shutting down the computer to avoid loss of data
Emerging trends in computer user environment
- Introduction of smartphones and small portable computers has made it easier for people to access computer services
- This means that the computer user environment is no longer confined within walls. It goes where a person has access to a computing device goes
- Mobile phone companies have made connectivity easy by availing network services to the people. This made it easy to access computer services anywhere at any time
Physical parts of a computer
What are the physical parts of a computer?

Functions of the physical part of a computer
- Monitor
Used to displaying information for example pictures and text
- Keyboard
Used for typing and giving instructions to the computer
- The system unit
Contains the devices oof a computer that Process data and gives information such as CPU
- Speakers and headphones
Are used for listening to music and audio files
- Printer
Is used for printing text on paper
- Mouse
Is used for selecting items and giving instructions to the computer by clicking
- Flash disks
Is used for storing and transferring information
- Scanner
Is used to take images of paper documents and displaying them on a computer
- Cables
Are used to connect different parts of a computer
Connecting the physical parts of the computer
Pupil’s activity
Page 45-46
How to minimise wastage in computer usage
- We can reuse or recycle the physical parts of a computer
For example
- If a device is in good working condition but longer in use it can be sold for some money to someone who will reuse it
Such devices can also be donated to people who need them
- A computer monitor can also be used as a television screen with little modification
- We can transform a system unit to a lockable cabinet by removing the inside components and installing a lock.
- Physical parts of a computer can be used to make art for example the keys of the keyboard
- The physical parts of a computer can be sent to the manufacturer or sent to a recycling centre where they are taken apart, their components sorted and recycled.
Interacting with physical parts of a computer
Pupil’s activity
Page 48-49
Hands on skills concepts
Starting a computer
- Switch on the power source
- Press the power button of the monitor then press the power button of the system unit to start your computer
Wait for the computer to finish the booting process
- Click on your user account. Type your username, enter your password and press enter to sign in to the computer
Shutting down a computer
- Close all the programs that may still be running
- Click on the start button and select the power button
- Click the power button. A window showing power option will appear
- Click shut down for the computer to undergo the shut down process
Function of the keys on a computer keyboard
- Delete (Del) key. It is used to erase characters to the right of the cursor, (i.e., from left to right).
- Esc
- Home
- Pg up
- Pg dn
- End
Backspace key – It has a backward arrow ( ) marked on it.√ Used to erase characters to the left of the cursor (i.e., from right to left on the same line). When pressed, it makes the cursor move one space backwards and the immediate letter or number to the left is erased.
- Crtl
- Tab
- Caps lock
- Enter
- Shift
A Cursor is a blinking underscore ( __ ) or a vertical beam (I ) that shows where the next character to be typed will appear.
Categories of keys of a computer keyboard

Alphanumeric keys
Keys are labeled with alphabetic letters A-Z, numbers arranged in a line 1,2, ……..0 respectively and symbols like:?,], % etc. This group also includes the following keys: cap lock, enter tab. space bar and backspace.
Caps lock key: Pressing this key let’s the user type in upper case-letters,(capitals) To switch back to lower case letters simply press the same key again.
Enter key (return key): Pressing this key forces the text cursor to move to the beginning of the next line. A cursor is a blinking underscore (-) or a vertical beam (I) that showswhere, the next character to be typed will appear. The enter key is also used to instruct .the computer to execute a command that has been selected on the screen.
Tab key: This key is used to move the text cursor at set intervals on the same line e.g. 10 mm, 20 mm etc.
The space bar: This bar creates a space between words during typing.
The backspace key: This key deletes characters from right to left on the same line.
Function keys
Function keys are usually located along the top of the keyboard. They are labeled FI, F2 up to FI2. They are used for tasks that occur frequently in various programs. For example pressing FI key in J most programs starts the HELP MENU.
Navigation and and editing keys – Cursor movement
Cursor movement keys are used to move the cursor on the screen. These keys are:
Arrow keys: Pressing the right or left arrow key moves the cursor one character to right or left respectively. Pressing the upward or downward arrow key moves the text cursor one line up or down respectively.
Page up and page down keys: Pressing page up key moves the cursor up one page in case the document has many pages. Pressing page down key moves the cursor down one page in case the document has many pages.
Home and end keys: Pressing home key moves the cursor to the beginning of the current line. Pressing end key moves the cursor to the end of the current line.
Editing keys are used to delete or insert characters in a document. These are:
Insert key: This key helps the user to insert or replace a character at the cursor position.
Delete (Del) key: This key deletes characters at the cursor position from left to right.
Special PC operation keys.
These keys are rarely used singly but in combination with other keys to give special instructions to the computer. They include SHIFT, CTRL, ALT and ESC keys.
Numeric keypad keys
The numeric keypad consists of a set of numbers 0 to 9 and the arithmetic signs like + (addition), (minus), * (multiplication) and / (division). They are located on the right hand side of the keyboard. The keypad is meant to help the user to rapidly enter numeric data. The numbers on the numeric keypad can only be used when the, situated on the numeric keypad, is turned on.
Use of pointing devices in a computer
- Most computers use a mouse as the main pointing devices.
- Laptops use a trackpad
- Other pointing devices that can be used with a computer are
- Trackball
- Pointing stick
- Joystick
- stylus
There are 5 common pointing devices operations
Clicking: This means pressing and releasing the left mouse button once. A click often selects an object.
Double clicking: This means pressing the left button twice in quick succession. Double clicking usually opens a file or starts a program
Right clicking: Pressing the right hand side mouse button once displays a list of commands from which the user can make a selection. This list of commands is called a shortcut menu or context sensitive menu. It is called a context sensitive menu because the commands on it apply to the right clicked item.
Drag and drop: This is whereby the user drags an item from one location on the screen to another. The procedure to accomplish this operation is as follows:
1. Point to the item you want to drag.
2. Press the left hand side mouse button and hold it down
3. Slide the mouse until the pointer reaches the desired position on the screen.
4. Finally release the mouse button and the item will be dropped in the new location.
Scrolling – the sliding movement of images, videos or text across a display screen either vertically or horizontally
Interacting with the keyboard and pointing devices of a computer
Pupil’s activity
Page 58-60
Computer system overview
A system – is a set of things working together to achieve a common goal or objective
A computer system – is a collection of parts that work together to receive, process, manage and present data and information
Identification of computer system components
The computer system consist of 3 components
- hardware
These are physical components of a computer system that you can touch
Examples: keyboard, mouse, monitor, CPU
- software
These are a set of instructions that direct a computer on what to do during processing.
They include operating system and programs like MS WORD, MS EXCEL
- liveware of peopleware
These are the users who command or direct computers to perform given task
This term also refers to the people that develop the software and hardware components of a computer
Functions of a computer components
- computer hardware
- accepts data and instructions
- process data
- stores data
- produces information
- communicates with devices and users
- computer software
- manages computer resources
- provides computer interface
- stores and retrieves data and instructions
- does mathematical calculation
- liveware
- designs and develops software and hardware
- operates a computer system
- enters data
- controls computer environment
Using computer system components
PUPIL’S ACTIVITY
PAGE 63
Linkage among components of a computer system
- The liverware uses hardware components to input data and give instructions to software
- The software in turn process the data and executes the instructions then gives the information through hardware.
- The information is then used by the liveware for decision making or fed back into the computer as data
Importance of computer systems in the society
- Business
Computer systems have enabled efficiency in record keeping, allowing long process to take a shorter time through automation.
They have also brought about online advertisement and sales using the internet
- Communication
Computers are connected through networks allowing for faster cheaper and safer communication across the globe
- Shopping
People today can shop online for goods and services and pay for them using online channels enabled by computer systems
- Socialising
Computer systems have made it possible for people to socialise and conduct viral meetings through various social media platforms
- Employment
Computer systems have provided employment opportunities
Eg software development and design
- Entertainment
People can access a variety of music, films and computer games on their computers
- Education
The internet is a huge information resources that is easily accessible compared to textbooks.
Learners are also able to learn online without the need to attend classes physically
Computer hardware concepts
Categories of hardware in a computer system
Computer hardware components are classified as
- Input devices
- Output devices
- CPU
- Storage devices
Functions of computer hardware categories
- Input devices
Enables user to enter data that needs processing and the instructions on how to process it
Examples: mouse, keyboard, touchpad, light pen, joystick, scanner, microphone
- CPU
Process the data entered into a computer according to the instructions
- Output devices
Present information that has been processed in different forms for example text, sound and pictures
Examples of output devices: monitor, printer, speakers, projector, plotter, headphones
- Storage devices
Saves data, information, computer software and running operations
Examples: hard disk, memory card, flash disk
Selecting appropriate hardware for different situations
Consider
- Reliability
- Cost
Using different elements of computer hardware
Pupil’s activity
Page 71-73
Input devices
Enables user to enter data that needs processing and the instructions on how to process it
Input devices in a computer system
Examples: mouse, keyboard, touchpad, light pen, joystick, scanner, microphone, barcode scanner, digital camera, capacitive and infra-red touch screens, 2D and 3D scanners
Categories of input devices
| Keying devices | Pointing devices | Digitiser | Scanning devices | Gaming controllers | Visual and imaging devices | Voice input devices |
| Keyboard | Mouse | Scanner | Barcode scanner | Joystick | Digital camera | microphone |
| Touchpad | Digital camera | 2D scanner | Steering wheel | Image scanner | ||
| Joystick | Microphone | 3D scanner | Video recorder | |||
| Touchscreen | ||||||
| Trackball |
Selecting appropriate input devices for different situations
When selecting input devices you can consider the following factors
- User needs
The device should meet the need of the user
- Cost
The device should be affordable according to user’s budget
- Functionality
Devices should serve the purpose it was intended
- User friendliness
The device should be easy to use
- Compatibility with hardware
Devices selected should be able to connect and work together with other available devices in the computer
- Level of expertise
Devices selected should meet the technical skills of the user.
Using input devices to perform tasks
Pupil’s activity
Page 77
Reusing input devices to minimise wastage
Input devices which are still functional can be used in the following ways
- Old and functional keyboards can be sold or donated to be reused with other compatible computer system
- Input devices which are in good condition and not in use can be donated to people who need them in the community
- Functional computer inputs can be used to set up other computers
- Obsolete and dysfunctional input devices can be sent to recycling facility where they will be recycled to make new products.
Central processing unit
The CPU is the part of a computer that process data
Locating the CPU in a computer system
Pupil’s activity
Page 80-81
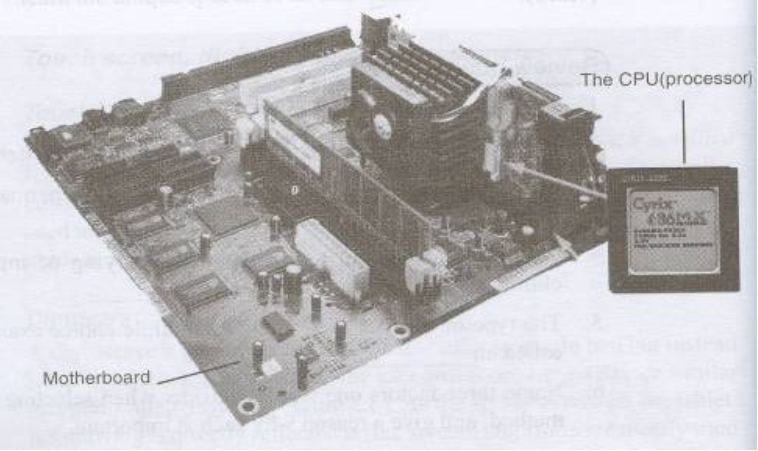
NB
Motherboard is a frame which holds and allows communication between the components of the computer system
The CPU is located on the motherboard
Functional elements of the CPU in a computer system
The CPU performs all types of data processing operations in a computer system
CPU has 3 components
- Control unit
- Arithmetic logic unit
- Special memory
Arithmetic and logic unit – ALU
Performs calculations like addition and subtraction
It also performs logical operations which mainly involve comparison of data
Control unit
Coordinates movement of data between the processor and the memory
Special memory
Stores data and information required during processing.
Most of the CPU operations are performed by the ALU
The control unit moves data between the ALU and the special memory and also tell the ALU what to do.
The ALU then process data and store the result in a special memory
Types of processors in computing devices
There are 6 types of CPU
CPUs are classified according to the number of cores they have
The core of a CPU receives instructions and perform calculations, or operations to satisfy the received instructions
| Type of processor | Number of cores | Examples |
| Single core | 1 | Intel 4004 |
| Dual core | 2 | Intel core duo, AMD X2 |
| Quad core | 4 | ATHLON II X4, INTEL CORE I3-10100 |
| Hexa core | 6 | INTEL CORE I5-11400, INTEL CORE I5-11600K |
| Octa core | 8 | INTEL CORE I7-11700K, INTEL CORE I7-11700 |
| Deca core | 10 | XEON SILVER 4114T |
Performing tasks using computers with different processors
Pupil’s activity
Page 84-85
- Processors receive input data, process it and generates results.
- It computes data and receives instructions in almost all actins carried out in a computer.
- Processors determines the speed with which a computing device processes information
- Computers with fast processors have high processing power and often give information faster
Output devices
Present information that has been processed in different forms for example graphics, tactile or text, sound (audio), video and pictures
Output devices of a computer system
Monitor, printer, speakers, projector, plotter, headphones, Braille embosser
Functions of output devices in a computer system
- Monitor
Display data in text and graphics
- Speakers
Gives information in form of sound
- Headphones
Produce audio information
- Printers
Produce text or picture information on a paper
- Projectors
Gives visual information by projecting it on a flat smooth surface like a wall or white board
- Plotters
Produces digital created graphics and drawings
Plotters use a pen to draw lines on paper
- Actuator
A part of a device or machine that helps to create physical movement using signals from a computer
- Braille embosser
A device that presses dots onto paper for people with visual impairment to read using their fingers
Categories of computer output devices
| Output devices | ||
| Visual output | Audio output | Physical output |
| Produces text or graphics | Produces sound | Produce movements |
| Monitor | Speakers | Printer |
| Screen | Headphones | Plotter |
| Projector | Earphones | Actuator |
| Braille embosser |
NB
- Hardcopy refers to data printed out on paper
It could be text, photographs, illustrations or any data that can be printed
| Advantage of hard copy | Disadvantage of hard copy |
| It is considered permanent data as editing and changing is not easy | It is expensive to produce as t requires paper, ink and printer |
| It does not need electricity, special devices or software to display | It is not easy to move from one place to another |
| When properly stored it is not easily lot | It requires a lot of physical storage space |
| It is not subjected to data stealing and cyber attacks | It can be stolen or destroyed through wear and tear or by environment factors such as fire, water |
- Soft copy is information stored and displayed in a computer
| Advantage of soft copy | Disadvantage of soft copy |
| It is easy to move from one place to another | It is vulnerable to cyber attacks and data theft |
| It is cheap to produce as it does not require paper or ink | It requires electricity, a device and software to display |
| Large amount of data and information can be stored without the need for a lot of physical space | It is considered temporary data which can be easily altered or manipulated |
| It is beneficial to the environment as it reduces the number of trees cut too make paper |
Selecting appropriate out devices
Factors that you consider when selecting output devices are
- Output quality
- User friendliness
- User needs
- Suitability to the function it is supposed to carry out
- Compatibility with the available devices
- The cost of purchasing and maintaining the output devices
Uses of output devices
We care and use output devices safely by
- Keeping the devices away from water and dust
- Avoiding exposure to foods and fluids
- Always powering off the devices after use
- Connecting only with compatible devices
- Cleaning and servicing the devices regularly
- Ensuring secure connection of the devices before use
Technological trends in development of output devices
Output devices have constantly been replace with new devices due to improved technology from innovators
Technological trends enables fast evolution of output devices which suit user needs better, are cost effective, friendly to the environment, secure and able to multitask
- Computer displays which are used to create clear, high quality, digital displays
- Wireless speakers and headphones which are more portable, have noise cancelling capability and produce better sound quality
- Better Braille embossers that give better quality Braille while producing very little noise. They also recognise speech and give speech feedback, making them user friendly
- Printers which produce better quality hardcopies, can be secured using passwords, are compact, cost effective and easy to use
Ports and cables
Port
A physical slot of a computer through which peripheral devices are connected.
All input and output devices of a computer are connected on the ports
Cable
A chord that connects and enables transfer of data or power from one device to another
A computing system has ports and cables that enable communication between the differebt components of a computer
Identifying cables and ports
Pupil’s activity
Page 97
Types of cables and ports used in a computer
There are 2 types of cables
- Power cables
These allow for power transmission and distribution from the source to all computer hardware components
- Data cables
These carry data and allows for communication between devices in a computing system
| Data cable | Description |
| USB cable and port | The universal serial bus is used to connect all devices to PCs like printers, keyboards, external hard disk, mice, scanners, cameras, and many more |
| PS/2 cable and ports | This is used to connect the keyboard and mouse to the computer. |
| Serial cable and port | This is used to connect hardware components such as mouse, doem and printer. It can also connect old models of computers together to allow the transfer of large files |
| Parallel cable and port | Parallel ports and cables connect computers and peripheral devices |
| Ethernet | This cable and ports connects the computer to a network and the internet |
| VGA cable and port | The VGA port and cable connects most computer models to their monitors |
| Audio cables and ports | This cable connects computers to audio devices such as speakers, headphones and microphones |
| RCA connectors | Digital output devices produce better quality audio. This is achieved using the RCA connectors |
| Digital video interface DVI cables and ports | DVI connects video source, such as a video display controller to a display device such as a computer monitor |
| HDMI port and cable | High definition media interface connects a computer to high definition and ultra high definition devices like computer monitors, HDTVs, BLU-RAY players, gaming consoles and high definition cameras |
Relate cables to their corresponding ports in a computer
Pupil’s activity
Page 100
Connecting cables to their corresponding ports
Pupil’s activity
Page 101-102
NB
- Ports enable the connection of output and input devices to a
- Ports allow computers to connect to networks
Computer setup
Setting up a computer is connecting all the hardware devices and preparing software programmes for a computer to function properly.
Problems experienced when setting up computers
- lack of skills in setting up computers
- difficulty matching cables to their respective ports
- inability to identify and correct failed connections
- lack of skills in installing operating systems
- lack of reliable power source to power devices
- damaged or broken cable pins due to improper fixing
eg forcing a cable to a wrong port
- damaged hardware devices that do not work
- computer and monitor not turning on due to faulty power cables or improper fixing of cables to the power supply
How to set up a computer
- setting up a new computer
- setting up a laptop
Pupil’s activity
Page 104-106
Setting up computers
The following are tools and equipments need for computer set up
- system unit
- Monitor
- Screwdriver
- Speakers
- Cables
- UPS
- Keyboard
- Power tester
- Surge protector
- Mouse
- Power extension cables
Some ways of ensuring safety when setting up computers include
- Ensure there is a stable power supply that can power on a computer before the connection
- Use a UPS or surge protector for power connection to the CPU and monitor
- Make sure your hands are completely dry to avoid electric shock and damaging any computer parts with moisture
- Handle all the parts of a computer with care. Place each component carefully on a hard flat surface. Be careful not to drop any parts
- Ensure your computer has enough room to allow for proper ventilation. If there is no free flow of air the computer can be damaged or cause fire.
- Be sure to connect all cables to the appropriate ports
- If a cable does not connect easily to a port, don’t forcefully push it in to avoid damaging it. Check that you are connecting it to the right port and that the pins and holes align
- Manage cables properly when setting up a computer. Ensure nothing is pressing on them and that they are not located in a place where they can be stepped on or tripped over
- Do not spill foods or liquids on the computer
- Always switch on the monitor before the CPU to display any errors or messages while booting
Setting up computers for use
Pupil’s activity
Page 109
Overcoming challenges experienced when setting up a computer
- Researching and learning how to set up a computer properly
- Researching and learning how to match cables to their respective parts checking that all connections are properly made
- Replacing or repairing damaged parts
- Ensuring that there is a reliable source of power
- Observing safety precautions when setting up a computer
Practising booting computers
- To tell that a computer is properly setup, we must switch it on and see if all the components are working well. This process is called booting up a computer
- The steps of booting a computer are as follows
- Switch on the main power supply on the socket
- If the computer is connected to the UPS, switch its power button on.
- Switch on the monitor by pressing the power button
- Switch on the system unit by pressing the power button
- Upon switching the system unit on , the computer performs a power on self test where the computer checks hat al components are connected and functioning well
- The computer then displays the name of the operating system followed by a display of icons on the computer monitor


It was nice thanks amigos